问题描述
c++中string作为参数是值拷贝,其他的对象也都是这样的么?
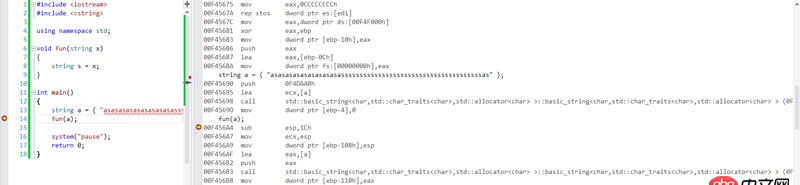
问题解答
回答1:c++中string作为参数是值拷贝?
是。
其他的对象也都是这样的么?
不一定,看拷贝/移动构造函数的定义是什么样的。例如:Value-like class 和 Pointer-like class。
回答2:题主既然都知道观察汇编窗口那么很容易就会发觉那里调用了该对象的的拷贝构造函数,所以这里是by value
实际上c++的对象都是作为by value的,如果需要by reference那你需要将函数签名改为const string& obj
回答3:1.若是将对象作为值参数传入函数,例如 func(const string obj),将会对对象进行拷贝复制,产生临时对象,影响性能;2.若是将对象作为引用或者指针传入参数,例如 func(const string &obj),fun(const string *obj),不会对象进行拷贝和复制,不会产生临时对象。
回答4:因为你传递参数的方式是按值传递的,所以调用的是拷贝构造函数,可以换成 string &x;这样就是传递引用了。另外c++11中新增加了可以用 string && x传递临时变量
回答5:C++中参数的传递方式是值拷贝(by value)还是引用拷贝(by reference)取决于你的形参命名方式。
示例一:按值传递。
/* function declaration of transferring argument by value */void func(string s) { // operates on string object s // note that here s is a copy of the string object you transferred in so any function-scope change will not affect invoker environment.}/* example usage of aforementioned function */string str;func(str);// after func call, str will keep the same
示例二:按引用传递。
/* function declaration */void func(string& s) { // operate on string object s // local change will be applied to the argument you transferred in}/* example usage */string str;func(str);// at this time, str will be changed with the modification func() made to it
示例三:按常量引用传递(在实际的工作中,这种调用方式是最常被使用的,它可以有效减少string拷贝的内存和CPU时间消耗)。
/* function declaration */void func(const string& s) { // transfer in a read-only reference of string object s // no copy will be made against s, neither any change allowed upon it}/* example usage */string str;func(str);// str is not supposed to be changed after func() invoke.


